
Managing this manually can be daunting and prone to oversight, especially in industries with strict regulatory requirements. Finally, after the payment has been authorized, the payment is processed, and the vendor receives their funds. This step often involves issuing checks, processing ACH payments, or executing credit card transactions.
Why manual AP workflows hold teams back
- Payment should be processed before or on the bill’s due date and may be done by check, electronic bank-to-bank payment, or credit card.
- Accounts payable represents money a company owes to its suppliers or vendors, while accounts receivable represents money owed to the company by its customers.
- AP automation will also help to reduce human errors and increase efficiency.
- AP often handles a supply of sales tax exemption certificates issued to managers to ensure qualifying business purchases don’t include sales tax expenses.
- For example, on 23 June 2019, the company ABC Ltd. purchases inventory for $1,500 on credit from XYZ Supply Co., one of its regular suppliers.
- An accounts payable invoice is a request for payment from a supplier to the accounts payable department.
Debit balance recovery refers to processes aimed at reclaiming such excess amounts. Accounts payable is a vital part of working capital management because it represents a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations while keeping enough cash for other investments. A clearly written and easily accessible AP policy document is a good start. To ensure your team follows processes to the letter, however, you need an accounts payable system that automates many of the most time-consuming steps—like BILL. Your accounts payable policy is the set of guidelines and procedures your organization establishes and follows to manage outstanding debts to suppliers and contractors (known as accounts payable). Clearly defined responsibilities for non-AP departments ensure timely invoice processing, purchase order handling, and adherence to proper documentation, enhancing overall efficiency.
Connect with our Sales team
- Since the financial crisis, trade credit in the form of accounts payable and accounts receivable has become a stable source of funding.
- Whether it’s a date, amount, or description, these have a waterfall effect that can lead to duplicate entries and inaccurate balances.
- Developing a routine for bill pay doesn’t just help the business’s bottom line and credibility with suppliers; it also gives you peace of mind knowing that everything is under control.
- It is especially important when firms find it challenging to obtain funding via financial or credit institutions.
- However, rising payables might also signal financial distress—a company might be delaying payments because it doesn’t have enough cash on hand to meet its obligations.
Every organization must have internal processes and control over the AP process to ensure the company’s cash and assets are safe. These internal controls help you to prevent paying a fraudulent or inaccurate invoice. Also, it avoids scenarios where you might pay the vendor twice for the same bill. Taking a closer look at your accounts payable might identify other issues with the business that need addressing. If you’re regularly behind on supplier payments, for example, you might find that you need to follow up with your own customers about their outstanding bills. Automated invoice processing saves you precious time by automatically scanning invoices and pre-filling pay details.
Your guide to accounts payable: Definition, process and examples
Seamless integration with ERP systems and enhanced reporting capabilities provide a comprehensive view of financial data, improving visibility and decision-making. An accounts payable ledger, is an accounting document where all transactional details are recorded in a systematic manner for future reference. It records transaction details like outstanding invoices that the entity will have to pay to its suppliers. This is a very important accounting book that helps the business to keep track of its cash flows in a systematic what does accounts payable mean manner. In simpler terms, an accounts payable ledger contains a detailed list of suppliers along with pertinent information such as invoice numbers, invoice dates, payment dates, and outstanding balances. This organized record-keeping is essential for maintaining financial accuracy and ensuring timely payments.
Accounts Payable (AP) vs. Accounts Receivable (AR): What’s the Difference?
Switch to digital payments to reduce costs, improve security, and streamline processes. This step involves determining when and how payment will be made, whether by check, ACH transfer, or credit card. Payment should be processed before or on the bill’s due date and may be done by check, electronic bank-to-bank payment, or credit card. After an invoice is approved, the accounts payable clerk may need to get authorization to make a payment.

However, it can also operate https://www.bookstime.com/ as a debit once the money is paid to the vendor. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) provide a framework of standards, guidelines, and procedures for financial accounting and reporting. When it comes to accounts payable, adhering to GAAP ensures accuracy, consistency, and transparency in your financial records. The amount payable is primarily an IOU (short-term liability) from one company to another. The creditor will record the transactions in their sub-ledger and general ledger as an asset called accounts receivable.
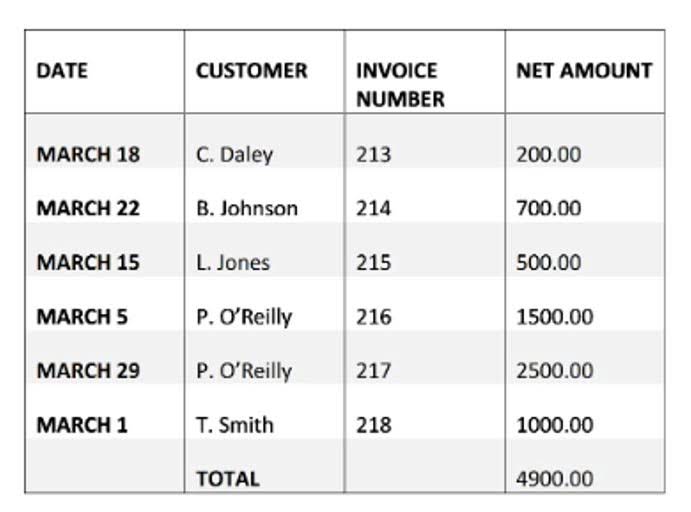
Accounts payable GL code report

The receipt includes a description and the number of items included in the shipment. Assume, for example, that Acme Manufacturing needs to order a $10,000 piece of machinery. To fully leverage the benefits of AP automation, it’s equally important to incorporate a set of solid practices that guide your day-to-day AP management. Just upload your form 16, claim your deductions and get your acknowledgment number online.
What is 3 Way Matching in Accounts Payable Process?

A well-functioning AP process helps maintain liquidity, optimizes working capital, and prevents costly penalties from late payments. Accounts payable are the sum of unpaid vendor invoices that appear in the balance sheet as a current liability. For example, if a company buys raw materials on credit, the amount owed to the supplier is recorded as accounts payable in the balance sheet. Automating the accounts payable process offers businesses the ability to streamline their ledger management, significantly reducing manual efforts and errors. With advanced QuickBooks ProAdvisor features like AI-powered invoice capture and automated invoice coding, finance teams can ensure real-time, accurate data processing.
- The exact type of raw materials that appear on your balance sheet may vary by your industry and even your business model.
- In the case of a regular vendor, the Vendor account will be debited instead of Accounts Payable.
- For example, a manufacturing company investing in new assembly-line machinery may receive equipment upfront but defer payment based on vendor terms, categorizing it under accounts payable.
- Accounts receivable on the other hand are an asset account, representing money that your customers owe you.
- The licensor provides the right to use the software for a year for a particular number of systems for a specific price.
- A balance sheet of a company offers a list of its financial position at a specific point in time.
Further, with the advent of AP automation, your organization offers transformative benefits like fraud prevention, scalability of business, and reduction of costs. The accounts payable refer to the full amount of debt that is owed by the company to its suppliers and vendors. This process ensures a strong customer-buyer relationship while optimizing the cash flow. In simple terms, accounts payable encompasses all of a company’s short-term debts or liabilities, while trade payables specifically refer to money owed for inventory-related goods or services.
